1) A production function is a relationship between inputs and
a. quantity of output.
b. revenue.
c. costs.
d. profit.
Answer: View Answer
2) 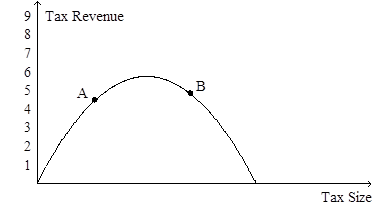
Refer to Figure 8-19. If the economy is at point B on the curve, then an increase in the tax rate will
a. increase the deadweight loss of the tax and increase tax revenue.
b. increase the deadweight loss of the tax and decrease tax revenue.
c. decrease the deadweight loss of the tax and increase tax revenue.
d. decrease the deadweight loss of the tax and decrease tax revenue.
Answer: View Answer
3) Table 12-1
On Taxable Income … The Tax Rate is …
Up to $8,375 10%
From $8,375 to $34,000 15
From $34,000 to $82,400 25
From $82,400 to $171,850 28
From $171,850 to $373,650 33
Over $373,650 35
Refer to Table 12-1. If Betina has $170,000 in taxable income, her marginal tax rate is
a. 25%.
b. 28%.
c. 33%.
d. 35%.
Answer: View Answer
4) Table 12-10
The following table shows the marginal tax rates for unmarried individuals for two years.
2009 2010
On Taxable Income… The Tax Rate is… On Taxable Income… The Tax Rate is…
$0 to $15,000 10% Over $0 20%
$15,000 to $40,000 15%
$40,000 to $75,000 20%
$75,000 to $120,000 25%
Over $120,000 30%
Refer to Table 12-10. Which of the following best describes the tax schedule in 2009?
a. proportional tax
b. progressive tax
c. regressive tax
d. vertical tax
Answer: View Answer
5) Table 14-6
The following table presents cost and revenue information for a firm operating in a competitive industry.
COSTS REVENUES
Quantity Produced Total Cost Marginal Cost Quantity Demanded Price Total Revenue Marginal Revenue
0 $100 — 0 $120 —
1 $150 1 $120
2 $202 2 $120
3 $257 3 $120
4 $317 4 $120
5 $385 5 $120
6 $465 6 $120
7 $562 7 $120
8 $682 8 $120
Refer to Table 14-6. What is the total revenue from selling 7 units?
a. $120
b. $490
c. $562
d. $840
Answer: View Answer
6) Mary and Cathy are roommates. Mary assigns a $30 value to smoking cigarettes. Cathy values smoke-free air at $15. Which of the following scenarios is a successful example of the Coase theorem?
a. Cathy offers Mary $20 not to smoke. Mary accepts and does not smoke.
b. Mary pays Cathy $16 so that Mary can smoke.
c. Mary pays Cathy $14 so that Mary can smoke.
d. Cathy offers Mary $15 not to smoke. Mary accepts and does not smoke.
Answer: View Answer
7) Which of the following firms is the closest to being a perfectly competitive firm?
a. the New York Yankees
b. Apple, Inc.
c. DeBeers diamond wholesalers
d. a wheat farmer in Kansas
Answer: View Answer
8) As government debt increases,
a. Congress will reduce spending by an equal proportion.
b. the government must spend more revenue on interest payments.
c. a trade-off with government deficits is inevitable.
d. tax rates must rise to cover the deficit.
Answer: View Answer
9) If a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market discovers that, at its current level of production, price is greater than marginal cost, it should
a. shut down.
b. reduce its output but continue operating.
c. continue to produce at the current levels.
d. increase its output.
Answer: View Answer
10) If the government were to limit the release of air-pollution produced by a steel mill to 75 parts per million, the policy would be considered a
a. regulation.
b. corrective tax.
c. subsidy.
d. market-based policy.
Answer: View Answer
11) 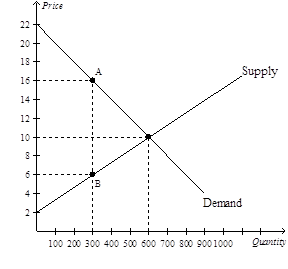
Refer to Figure 8-6. Total surplus with the tax in place is
a. $1,500.
b. $3,600.
c. $4,500.
d. $6,000.
Answer: View Answer
12) European countries tend to rely on which type of tax more so than the United States does?
a. an income tax
b. a lump-sum tax
c. a value-added tax
d. a corrective tax
Answer: View Answer
13) 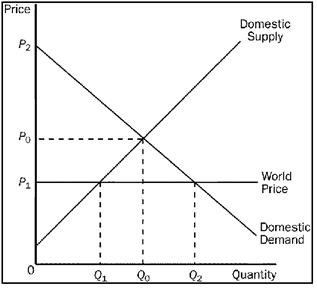
Refer to Figure 9-10. With trade, the equilibrium price of rifles and the equilibrium quantity of rifles demanded in Mexico are
a. P1 and Q1.
b. P1 and Q2.
c. P2 and Q2.
d. P0 and Q0.
Answer: View Answer
14)
Refer to Figure 10-9, Panel (b) and Panel (c). The installation of a scrubber in a smokestack reduces the emission of harmful chemicals from the smokestack. Therefore, the socially optimal quantity of smokestack scrubbers is represented by point
a. Q2.
b. Q3.
c. Q4.
d. Q5.
Answer: View Answer
15) 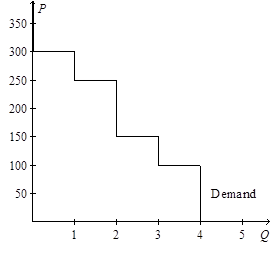
Refer to Figure 7-1. If the price of the good is $200, then
a. consumer surplus is $150.
b. consumer surplus is $650.
c. producer surplus is $650.
d. producer surplus is $750.
Answer: View Answer
16) 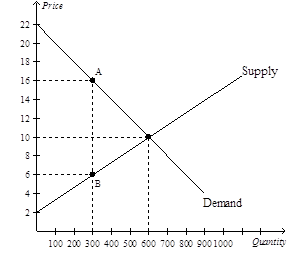
Refer to Figure 8-6. When the tax is imposed in this market, buyers effectively pay what amount of the $10 tax?
a. $0
b. $4
c. $6
d. $10
Answer: View Answer
17) 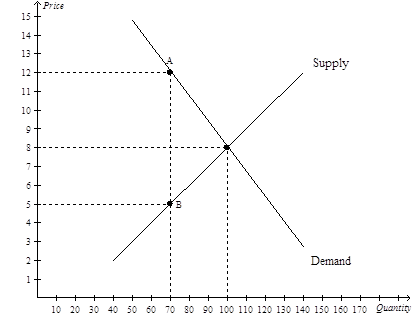
Refer to Figure 8-4. The tax results in a loss of producer surplus that amounts to
a. $45.
b. $90.
c. $210.
d. $255.
Answer: View Answer
18) 
Refer to Figure 7-21. Buyers who value this good more than the equilibrium price are represented by which line segment?
a. AC.
b. CK.
c. BC.
d. CH.
Answer: View Answer
19) Table 13-4
Charless Math Tutoring
Number of Workers Output (number of students tutored per week)
0 0
1 20
2 45
3 60
4 70
Refer to Table 13-4. What is the marginal product of the third worker?
a. 15 students
b. 20 students
c. 35 students
d. 60 students
Answer: View Answer
20) The French expression used by free-market advocates, which literally translates as “allow them to do,” is
a. laissez-faire.
b. je ne sais pas.
c. si’l vous plait.
d. tte–tte.
Answer: View Answer
21) Suppose a competitive market is comprised of firms that face identical cost curves. The firms experience an increase in demand that results in positive profits for the firms. Which of the following events are then most likely to occur?
(i) New firms will enter the market.
(ii) In the short run, price will rise; in the long run, price will rise further.
(iii) In the long run, all firms will be producing at their efficient scale.
a. (i) and (ii) only
b. (i) and (iii) only
c. (ii) and (iii) only
d. (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer: View Answer
22)
Refer to Figure 10-19. Which of the following quantities decreases as the quantity of the good is increased?
a. the private cost of the good
b. the social cost of the good
c. the private value of the good
d. the external benefit of the good
Answer: View Answer
23) Which of the following represents a potential solution to the problem of environmental pollution?
a. corrective taxes
b. well established property rights
c. government regulation
d. All of the above are correct.
Answer: View Answer
24) Table 12-12
United States Income Tax Rates for a Single Individual, 2009 and
2009 Tax Rates Income Ranges 2010 Tax Rates Income Ranges
15% $0 $28,000 10% $0 $10,000
28% $28,000 $70,000 15% $10,000 $30,000
31% $70,000 $140,000 27% $30,000 $60,000
36% $140,000 $300,000 30% $60,000 $150,000
40% over $300,000 35% $150,000 $320,000
38% over $320,000
Refer to Table 12-12. What type of tax structure did the United States have in 2009 for single individuals?
a. A proportional tax structure
b. A regressive tax structure
c. A progressive tax structure
d. A lump-sum tax structure
Answer: View Answer
25) It would always be a mistake to view
a. many species of animals as common resources.
b. a road as a public good.
c. national defense as a common resource.
d. a fireworks display as a public good.
Answer: View Answer
26) Which of the following are taxed?
a. both corporate profits and dividends shareholders receive
b. corporate profits but not dividends shareholders receive
c. dividends shareholders receive but not corporate profits
d. neither corporate profits nor dividends shareholders receive
Answer: View Answer
27) Table 13-15
Consider the following table of long-run total cost for four different firms:
Quantity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Firm 1 $210 $340 $490 $660 $850 $1,060 $1,290
Firm 2 $180 $350 $510 $660 $800 $930 $1,050
Firm 3 $120 $250 $390 $540 $700 $870 $1,050
Firm 4 $150 $300 $450 $600 $750 $900 $1,050
Refer to Table 13-13. Which firm has constant returns to scale over the entire range of output?
a. Firm 1
b. Firm 2
c. Firm 3
d. Firm 4
Answer: View Answer
28) 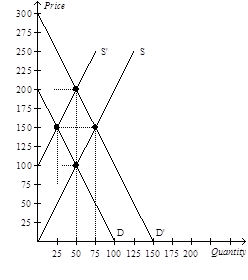
Refer to Figure 7-9. If the supply curve is S and the demand curve shifts from D to D, what is the increase in producer surplus to existing producers?
a. $625
b. $2,500
c. $3,125
d. $5,625
Answer: View Answer
29) Scenario 13-9
Jessica makes photo frames. She spends $5 on the materials for each photo frame. She can create one photo frame in an hour. She earns $10 per hour at a part-time job at the local coffee shop. She can sell a photo frame for $30 each.
Refer to Scenario 13-9. An economist would calculate the total cost for one photo frame to be
a. $5.
b. $10.
c. $15.
d. $25.
Answer: View Answer
30) Some costs do not vary with the quantity of output produced. Those costs are called
a. marginal costs.
b. average costs.
c. fixed costs.
d. explicit costs.
Answer: View Answer
31) Laws that are passed that either require or forbid certain behaviors are examples of command-and-control policies.
Answer: View Answer
32) Tolls are not effective in altering people’s incentives to drive during rush hour.
Answer: View Answer
33) Because the benefits of basic research are obvious and easy to measure, it is likely that the public sector pays for the right amount and the right kinds of basic research.
Answer: View Answer
34) Corporate income taxes are based on the amount of revenue a corporation earns.
Answer: View Answer
35) The shape of the total-cost curve is inversely related to the shape of the production function.
Answer: View Answer
36) Adam Smith describes a visit to a car factory when discussing economies of scale in his book An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations.
Answer: View Answer
37) Economists agree that trade ought to be restricted if free trade means that domestic jobs might be lost because of foreign competition.
Answer: View Answer
38) The production function depicts a relationship between which two variables? Also, draw a production function that exhibits diminishing marginal product.
Answer: View Answer
39) All competitive firms earn zero economic profit in both the short run and the long run.
Answer: View Answer
40) A good that is rival in consumption is one that someone can be prevented from using if she did not pay for it.
Answer: View Answer