1) 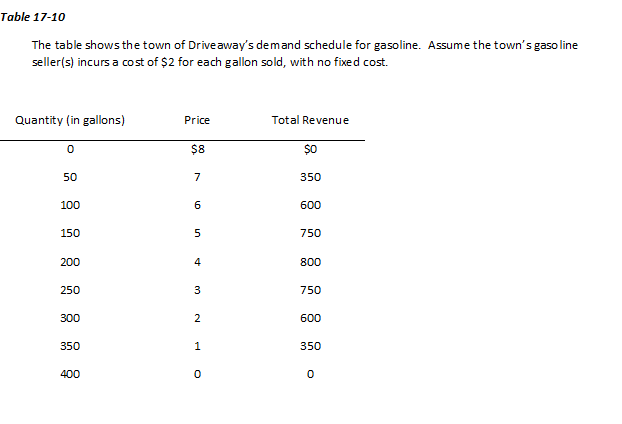
Refer to Table 17-10. Suppose we observe that the price of a gallon of gasoline in Driveaway is $5; we observe as well that a particular sellers profit is $150. Given this observation, which of the following scenarios is most likely?
a. The market for gasoline in Driveaway is a monopoly.
b. There are two identical sellers of gasoline in Driveaway, and the sellers collude.
c. There are two identical sellers of gasoline in Driveaway, and the sellers do not collude.
d. There are three identical sellers of gasoline in Driveaway, and the sellers collude.
Answer: View Answer
2) Suppose that you have $100 today and expect to receive $100 one year from today. Your money market account pays an annual interest rate of 25%, and you may borrow money at that interest rate. If you save all your money, how much money will you have one year from today?
a. $100
b. $125
c. $200
d. $225
Answer: View Answer
3)
Refer to Figure 21-24. Anna experiences an increase in her hourly wage. Her optimal choice point moves from A to B. For Anna,
a. her labor supply curve is backward bending.
b. her labor supply curve is upward sloping.
c. leisure is an inferior good.
d. both a and c are correct.
Answer: View Answer
4) Which of the following statements is correct for both a monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm?
i) The firm maximizes profits by equating marginal revenue with marginal cost.
ii) The firm maximizes profits by equating price with marginal cost.
iii) Demand equals marginal revenue.
iv) Average revenue equals price.
a. i), iii), and iv) only
b. i) and iv) only
c. i), ii), and iv) only
d. i), ii), iii), and iv)
Answer: View Answer
5) 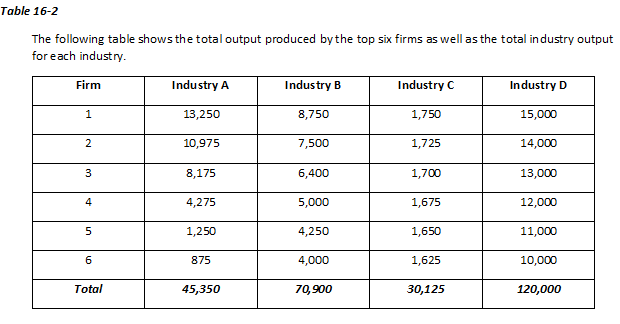
Refer to Table 16-2. What is the concentration ratio for Industry D?
a. about 13%
b. about 35%
c. about 45%
d. about 63%
Answer: View Answer
6) 
Refer to Figure 17-4. If the two companies make their pricing decisions independently, then it is likely that Bilco will
a. charge a low price only if Acme charges a low price.
b. charge a low price only if Acme charges a high price.
c. charge a low price regardless of whether Acme charges a high price or a low price.
d. None of the above are correct.
Answer: View Answer
7) The general term for market structures that fall somewhere between monopoly and perfect competition is
a. incomplete markets.
b. imperfectly competitive markets.
c. oligopoly markets.
d. monopolistically competitive markets.
Answer: View Answer
8)
Refer to Figure 21-17. It would be possible for the consumer to reach I2 if
a. the price of Y decreases.
b. the price of X decreases.
c. income increases.
d. All of the above would be correct.
Answer: View Answer
9) When quality cannot be easily judged in advance, what provides consumers with information about the quality of a product?
a. a brand name
b. a tie-in
c. the quantity available for sale
d. the amount of deadweight loss
Answer: View Answer
10) A consumer consumes two normal goods, popcorn and Pepsi. The price of Pepsi rises. The substitution effect, by itself, suggests that the consumer will consume
a. more popcorn and more Pepsi.
b. less popcorn and less Pepsi.
c. more popcorn and less Pepsi.
d. less popcorn and more Pepsi.
Answer: View Answer
11) Which of the following is a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
a. ownership of a key resource by a single firm
b. free entry
c. identical product
d. patents
Answer: View Answer
12) Which of the following does not represent a tradeoff facing a consumer?
a. choosing to purchase more of all goods
b. choosing to spend more time on leisure and less time on work
c. choosing to spend more now and consume less in the future
d. choosing to purchase less of one good in order to purchase more of another good
Answer: View Answer
13) Draw a budget constraint that is consistent with the following prices and income.
Income = 200
PY = 50
PX = 25
a. Demonstrate how your original budget constraint would change if income increases to 500.
b. Demonstrate how your original budget constraint would change if PY decreases to 20.
c. Demonstrate how your original budget constraint would change if PX increases to 40.
Answer: View Answer
14) The following diagram shows one indifference curve representing the preferences for goods X and Y for one consumer.
What is the marginal rate of substitution between points A and B?
a. 1/2
b. 4/3
c. 2
d. 3
Answer: View Answer
15) Liberalism aims to raise the welfare of the worst-off person in society. This rule is called the
a. minimax regret criterion.
b. conservative approach.
c. Nozick criterion.
d. maximin criterion.
Answer: View Answer
16) Which of the following conditions is characteristic of a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium?
a. P > MR and P = MC
b. ATC = demand and MR = MC
c. P < MC and demand = ATC
d. P > ATC and demand > MR
Answer: View Answer
17) An important difference between the situation faced by a profit-maximizing monopolistically competitive firm in the short run and the situation faced by that same firm in the long run is that in the short run,
a. price may exceed marginal revenue, but in the long run, price equals marginal revenue.
b. price may exceed marginal cost, but in the long run, price equals marginal cost.
c. price may exceed average total cost, but in the long run, price equals average total cost.
d. there are many firms in the market, but in the long run, there are only a few firms in the market.
Answer: View Answer
18) For the economy as a whole, spending on advertising comprises about what percent of total firm revenue?
a. 0.5
b. 2
c. 10
d. 20
Answer: View Answer
19) Which of the following statements is true of wages, educational attainment, and gender?
a. Male workers are compensated for attending college, while female workers generally are not.
b. Female workers are compensated for attending college, while male workers generally are not.
c. Both genders receive a higher wage for attending college.
d. Neither gender receives a higher wage for attending college.
Answer: View Answer
20) 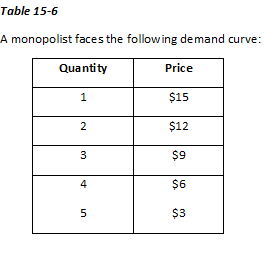
Refer to Table 15-6. Suppose the monopolist has total fixed costs equal to $5 and a variable cost equal to $4 per unit for all units produced. What would the total profit be if she charged $6 per unit for her product?
a. $1
b. $3
c. $8
d. $15
Answer: View Answer
21) 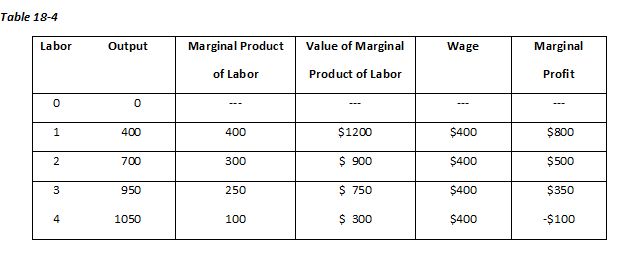
Refer to Table 18-4. The price of output is
a. $1.
b. $2.
c. $3.
d. $400.
Answer: View Answer
22) Adverse selection is
a. the tendency of a person who is imperfectly monitored to engage in dishonest or otherwise undesirable behavior.
b. an action taken by an uninformed party to induce an informed party to reveal information.
c. the failure of majority voting to produce transitive preferences for society.
d. the tendency for the mix of unobserved attributes to become undesirable from the standpoint of an uninformed party.
Answer: View Answer
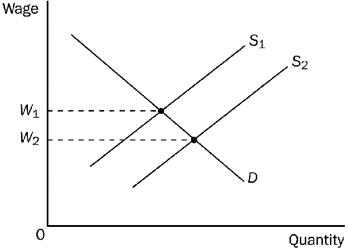
23) 
Scenario 18-5
Suppose that workers from northern Minnesota, North Dakota, and Montana decide to emigrate to southern Canada.
Refer to Figure 18-7. Assume W1 = $20 and W2 = $18, and the market is always in equilibrium. A shift of the labor supply curve from S1 to S2 would
a. increase the value of the marginal product of labor by $2.
b. decrease the value of the marginal product of labor by $2.
c. decrease the value of the marginal product of labor by more than $2.
d. not change the value of the marginal product of labor.
Answer: View Answer
24) Scenario 16-3
Suppose market demand for a product is given by the equation P = 20 Q. For this market demand curve, marginal revenue is MR = 20 2Q.
Refer to Scenario 16-3. If the marginal cost of producing this good is 0, what price would a profit-maximizing monopolist charge for the product?
a. P = 0
b. P = 5
c. P = 10
d. P = 20
Answer: View Answer
25) 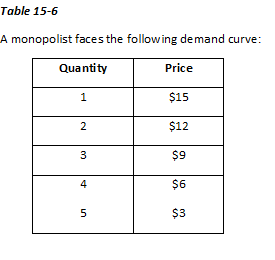
Refer to Table 15-6. If the monopolist has a constant marginal cost for her product equal to $7, what is her profit-maximizing price?
a. $6
b. $9
c. $12
d. $15
Answer: View Answer
26) When Phils income increases, he purchases fewer spaghetti dinners than he did before his income increased. For Phil, spaghetti dinners are a(n)
a. normal good.
b. inferior good.
c. optimal good.
d. luxury good.
Answer: View Answer
27) Among the people who are characterized below, who has the highest opportunity cost of leisure?
a. an attorney who earns $200 per hour and who plays golf during her leisure time
b. a medical doctor who earns $210 per hour and who sleeps during his leisure time
c. a retail clerk who earns $15 per hour and who watches TV during her leisure time
d. a waiter who earns $12 per hour and who reads poetry during his leisure time
Answer: View Answer
28) Resale price maintenance involves a firm
a. colluding with another firm to restrict output and raise prices.
b. selling two individual products together for a single price rather than selling each product individually at separate prices.
c. temporarily cutting the price of its product to drive a competitor out of the market.
d. requiring that the firm reselling its product do so at a specified price.
Answer: View Answer
29) Karen, Tara, and Chelsea each buy ice cream and paperback novels to enjoy on hot summer days. Ice cream costs $5 per gallon, and paperback novels cost $8 each. Karen has a budget of $80, Tara has a budget of $60, and Chelsea has a budget of $40 to spend on ice cream and paperback novels. Who can afford to purchase 4 gallons of ice cream and 5 paperback novels?
a. Karen, Tara, and Chelsea
b. Karen only
c. Karen and Tara but not Chelsea
d. none of the women
Answer: View Answer
30) In 1913, the Ford Motor Company decided to pay its employees $5 a day. This wage was significantly higher than what any other organization offered. Henry Ford believed that this wage would make his employees happier, increase their productivity, and lower employee turnover. Economists would say that Mr. Ford offered his employees
a. a union.
b. an efficiency wage.
c. a diminishing rate of marginal return.
d. a leisure wage.
Answer: View Answer
31) The poverty rate is based on a familys
a. income, in-kind transfers, and other government aid.
b. income and in-kind transfers.
c. in-kind transfers only.
d. income only.
Answer: View Answer
32) At the profit-maximizing quantity of output for a monopolist, average revenue, marginal revenue, and price are all equal.
Answer: View Answer
33) Superstars earn high incomes due to their ability to satisfy the demands of millions of people at once.
Answer: View Answer
34) Explain the role that consumers play in perpetuating discrimination in labor markets.
Answer: View Answer
35) Monopolistic competition is characterized by many buyers and sellers, product differentiation, and free entry.
Answer: View Answer
36) Giffen goods are inferior goods for which the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
Answer: View Answer
37) The Condorcet paradox demonstrates that the order in which people vote on choices may influence the final outcome.
Answer: View Answer