1) The quarterly sales for specific educational software over the past
three years are given in the following table. Compute the four
seasonal factors.
| YEAR 1 | YEAR 2 | YEAR 3 | |
| Quarter 1 | 1710 | 1820 | 1830 |
| Quarter 2 | 960 | 910 | 1090 |
| Quarter 3 | 2720 | 2840 | 2900 |
| Quarter 4 | 2430 | 2200 | 2590 |
Answer: View Answer
2) The UNFCCC works on the “cap-and-trade” principle.
Answer: View Answer
3) The Shamrock Transportation Company has four terminals: A, B, C,
and D. At the start of a particular day, there are 8, 8, 6, and 3
tractors available at those terminals, respectively. During the
previous night, trailers were loaded at plants R, S, T, and U. The
number of trailers at each plant is 2, 12, 5, and 6, respectively.
The company dispatcher has determined the distances between each
terminal and each plant, as follows. How many tractors should be
dispatched from each terminal to each plant in order to minimize
the total number of miles traveled?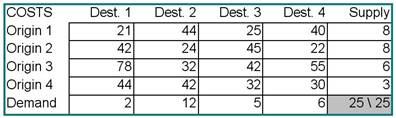
Answer: View Answer
4) What is a product-by-value analysis, and what type of decisions
does it help managers make?
Answer: View Answer
5) Compare the chase strategy versus level scheduling.
Answer: View Answer
6) The specification for a plastic liner for concrete highway projects
calls for a thickness of 6.0 mm 0.1 mm. The standard deviation of
the process is estimated to be 0.02 mm. What are the upper and
lower specification limits for this product? The process is known
to operate at a mean thickness of 6.03 mm. What is the Cpand Cpkfor
this process? About what percent of all units of this liner will
meet specifications?
Answer: View Answer
7) The constant work-in-process (ConWIP) card aids input-output
control by limiting the amount of work in a work center.
Answer: View Answer
8) Gantt charts are useful for scheduling jobs, but not for loading
them.
Answer: View Answer
9) A component must have reliability of .9925. Two technologies are
available for this component: one produces a component with .999
reliability at a cost of $2000. Another produces a component with
.73 reliability at a cost of $450. Which is cheaper: one high
quality component or a parallel set of inferior components? (Hint:
for the inferior components, you first need to determine the number
of them that would be needed to ensure overall reliability of
.9925.)
Answer: View Answer
10) Low-cost leadership is the ability to distinguish the offerings of
the organization in a way that the customer perceives as adding
value.
Answer: View Answer
11) Normal time is always less than the average observed time.
Answer: View Answer
12) CentralUniversity uses $123,000 of a particular toner cartridge for
laser printers in the student computer labs each year. The
purchasing director of the university estimates the ordering cost
at $45 and thinks that the university can hold this type of
inventory at an annual storage cost of 22% of the purchase price.
How many months’ supply should the purchasing director order at one
time to minimize the total annual cost of purchasing and carrying?
Answer: View Answer
13) By starting random number intervals at 01, not 00, the top of each
range is the cumulative probability.
Answer: View Answer
14) How do many electronic firms deal with infant mortality in their
products?
Answer: View Answer
15) Operations managers are finding online auctions a fertile area for
disposing of discontinued inventory.
Answer: View Answer
16) Explain how a load-distance model helps solve problems in process
layout.
Answer: View Answer
17) The higher the process capability ratio, the greater the likelihood
that process will be within design specifications.
Answer: View Answer
18) To measure the voltage of batteries, one would sample by
attributes.
Answer: View Answer
19) McDaniel Shipyards wants to develop a control chart to assess the
quality of its steel plate. They take ten sheets of 1″ steel plate
and compute the number of cosmetic flaws on each roll. Each sheet
is 20′ by 100′. Based on the following data, develop limits for the
3-sigma control chart, plot the control chart, and determine
whether the process is in control.
| Sheet | Number of flaws |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 5 |
| 7 | 0 |
| 8 | 2 |
| 9 | 0 |
| 10 | 2 |
Answer: View Answer
20) A Gantt load chart shows the loading and idle time of several
departments, machines, or facilities.
Answer: View Answer
21) Which of the following is the prescribed remedy when the bullwhip
effect is caused by shortage gaming?
A) share demand information
B) channel coordination
C) increase capacity
D) price stabilization
E) allocate orders based on past demand
Answer: View Answer
22) Jack’s Refrigeration Repair is under contract to repair,
recondition, and/or refurbish commercial and industrial icemakers
from restaurants, seafood processors, and similar organizations.
Jack currently has five jobs to be scheduled, shown in the order in
which they arrived.
| Job | Processing Time (hours) | Due (hours) |
| V | 20 | 50 |
| W | 10 | 35 |
| X | 50 | 90 |
| Y | 15 | 35 |
| Z | 55 | 75 |
(a) Complete the following table. (Show your supporting
calculations below).
(b) Which dispatching rule has the best score for flow time?
(c) Which dispatching rule has the best score for work-in-process
(jobs in the system)?
(d) Which dispatching rule has the best score for lateness?
| Dispatching Rule | Job Sequence | Average Flow Time | Average Number of Jobs | Average Lateness |
| FCFS | ||||
| SPT | ||||
| EDD | ||||
| CR |
Answer: View Answer
23) A task involves positioning two metal parts with a rubber gasket
sandwiched between them, inserting two bolts into predrilled holes,
threading a nut onto each bolt, and tightening each bolt with a
pneumatic wrench. In a preliminary study, the manager observed one
of his workers performing this task five times. The observations
were made in an air-conditioned, well-lit training facility, at
ground level, with all tools and equipment clean and readily
available.
| Observation: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Task time (seconds): | 50 | 54 | 60 | 66 | 56 |
a. What is the average observed time for this task?
b. What is the normal time for this task if the employee worked at
a 10% slower pace than is typical for adequately trained
workers?
c. What is standard time for this task if allowances sum to 14%?
Answer: View Answer
24) The proper quantity of safety stock is typically determined by:
A) using a single-period model
B) carrying sufficient safety stock so as to eliminate all
stockouts
C) multiplying the EOQ by the desired service level
D) setting the level of safety stock so that a given stockout risk
is not exceeded
E) minimizing total costs
Answer: View Answer
25) What combination of x and y will yield the optimum for this
problem?
Maximize $3x + $15y, subject to (1) 2x + 4y 12 and (2) 5x + 2y 10
and (3) x, y 0.
A) x = 2, y = 0
B) x = 0, y = 3
C) x = 0, y = 0
D) x = 1, y = 5
E) x = 0, y = 5
Answer: View Answer
26) A manager wants to build 3-sigma x-bar control limits for a
process. The target value for the mean of the process is 10 units,
and the standard deviation of the process is 6. If samples of size
9 are to be taken, what will be the upper and lower control limits,
respectively?
A) -8 and 28
B) 16 and 4
C) 12 and 8
D) 4 and 16
E) 8 and 12
Answer: View Answer
27) Solving a load-distance problem for a process-oriented layout
requires that:
A) the difficulty of movement be the same for all possible
paths
B) pickup and setdown costs vary from department to department
C) the cost to move a load be the same for all possible paths
D) takt time be less than 1
E) Proplanner software examines all possible department
configurations
Answer: View Answer
28) A contractor’s project being analyzed by PERT has an estimated time
for the critical path of 120 days. The sum of all activity
variances is 81; the sum of variances along the critical path is
What is the probability that the project will take 130 or more days
to complete?
A) 0.1057
B) 0.1335
C) 0.8512
D) 0.8943
E) 1.29
Answer: View Answer
29) Which critical ratio value implies that a job is already late?
A) more than 100
B) 1
C) less than 1
D) 10
E) 3.4
Answer: View Answer
30) A manager is comparing the total maintenance (preventive plus
breakdown) cost curves for two scenarios. The graphs have
maintenance commitment on the x-axis and costs on the y-axis.
Scenario A includes the direct breakdown maintenance costs, while
Scenario B includes the “full” (direct and indirect) breakdown
maintenance costs. Which of the following should the manager notice
when going from Scenario A to Scenario B?
A) Total cost is decreased
B) Optimal point is moved to the left
C) Optimal point is moved to the right
D) Preventative maintenance cost slope is increased
E) None of the above
Answer: View Answer
31) Which of the following activities takes place most immediately once
the mission has been developed?
A) The firm develops alternative or back-up missions in case the
original mission fails
B) The functional areas develop their functional area
strategies
C) The functional areas develop their supporting missions
D) The ten OM decision areas are prioritized
E) Operational tactics are developed
Answer: View Answer
32) In a minimization problem, a positive improvement index in a cell
indicates that:
A) the solution is optimal
B) the total cost will increase if units are reallocated to that
cell
C) there is degeneracy
D) the total cost will decrease if units are reallocated to that
cell
E) the problem has no feasible solution
Answer: View Answer
33) What value of the bullwhip measure would indicate that the bullwhip
effect exists?
A) greater than 1
B) greater than 0
C) less than 0
D) less than 1
E) 1
Answer: View Answer
34) Which of the following companies use a mass customization
approach?
A) Dell
B) Align Technology
C) Frito-Lay
D) Arnold Palmer hospital
E) A and B
Answer: View Answer
35) Service times in an automobile repair shop tend to follow which
probability distribution?
A) exponential
B) normal
C) triangular
D) binomial
E) Erlang
Answer: View Answer
36) Net present value will be greater:
A) as a fixed set of cash receipts occurs later rather than
earlier
B) if the future value of a cash flow is smaller
C) for one end-of-year receipt of $1200 than for twelve monthly
receipts of $100 each
D) for a 4% discount rate than for a 6% discount rate
E) All of the above are true
Answer: View Answer
37) Therbligs are:
A) the smallest unit of time used in methods time measurement
exercises
B) the largest unit of time used in methods time measurement
exercises
C) basic physical elements of motion as used in methods time
measurement exercises
D) the full range of motions required to complete a job as used in
methods time measurement exercises
E) the smallest amount of time required to complete a job
Answer: View Answer
38) Two critical path activities are candidates for crashing on a CPM
network. Activity details are in the table below. To cut one day
from the project’s duration, activity ________ should be crashed
first, adding ________ to project cost.
| Activity | Normal Time | Normal Cost | Crash Time | Crash Cost |
| B | 4 days | $6,000 | 3 days | $8,000 |
| C | 6 days | $4,000 | 4 days | $6,000 |
A) B; $2,000
B) B; $8,000
C) C; $1,000
D) C; $2,000
E) C; $6,000
Answer: View Answer
39) The objective of aggregate planning is to meet forecast demand
while ________ over the planning period.
A) minimizing cost
B) maximizing service level
C) minimizing stock out
D) minimizing fixed cost
E) all of the above
Answer: View Answer
40) An x-bar control chart was examined and no data points fell outside
of the limits. Can this process be considered in control?
A) Not yet, there could be a pattern to the points
B) Not yet, the R-chart must be checked
C) Not yet, the number of samples must be known
D) Yes
E) Both A and B
Answer: View Answer
41) Which of the following is not a typical inspection point?
A) upon receipt of goods from your supplier
B) when production or service is complete
C) before the product is shipped to the customer
D) at the supplier’s plant while the supplier is producing
E) after a costly process
Answer: View Answer
42) A local club is selling Christmas trees and deciding how many to
stock for the month of December. If demand is normally distributed
with a mean of 100 and standard deviation of 20, trees have no
salvage value at the end of the month, trees cost $20, and trees
sell for $50 what is the service level?
A) .60
B) .20
C) .84
D) .40
E) unable to determine given the above information
Answer: View Answer
43) Which of the following aggregate planning strategies is a capacity
option?
A) influencing demand by changing price
B) counterseasonal product mixing
C) influencing demand by extending lead times
D) changing inventory levels
E) influencing demand by back ordering
Answer: View Answer
44) Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of a Model C or
M/D/1 system?
A) single server
B) single phase
C) Poisson arrival rate pattern
D) exponential service time pattern
E) unlimited population size
Answer: View Answer
45) A local university is considering changes to its class structure in
an effort to increase professor productivity. The old schedule had
each professor teaching 5 classes per week, with each class meeting
an hour per day on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. Each class
contained 20 students. The new schedule has each professor teaching
only 3 classes, but each class meets daily (Mon.-Fri.) for an hour.
New classes contain 50 students.
a. Calculate the labor productivity for the initial situation
(students/hour).
b. Calculate the labor productivity for the schedule change
(students/hour).
c. Are there any ethical considerations that should be accounted
for?
d. Suppose that each teacher also is required to have 2 hours of
Office Hours each day he/she taught class. Is the schedule change a
productivity increase?
Answer: View Answer
46) There are three work centers (A, B, and C) behind the financial aid
counter at a nearby university. They can each fit into any of three
office spaces (1, 2, and 3) off the corridor behind the desk. There
is no student contact in these areas, only workers. The distance
1-2 is 20 feet, 2-3 is 30 feet, and 1-3 is 50 feet. The matrix of
work (trips per day) at the three centers are shown in the
following table. Remember that each trip must be a round-trip (from
1 to 2 and back, for example).
| A | B | C | |
| A | — | 20 | 0 |
| B | 45 | — | 25 |
| C | 60 | 0 | — |
(a) How many possible assignments are there? List them.
(b) Calculate the total distance traveled in each of these
assignments.
(c) Which assignment minimizes distance traveled?
Answer: View Answer
47) Among the tools of TQM, the tool ordinarily used to aid in
understanding the sequence of events through which a product
travels is a:
A) Pareto chart
B) flowchart
C) check sheet
D) Taguchi map
E) poka-yoke
Answer: View Answer
48) A system has three components in series with reliabilities 0.9, 7,
and 0.5. What is the system reliability?
A) 0.315
B) 0.500
C) 0.700
D) 0.900
E) 2.100
Answer: View Answer
49) Flow diagrams are used to analyze:
A) movement of people or material
B) utilization of an operator and machine
C) body movements
D) time taken by various activities
E) unnecessary micro-motions
Answer: View Answer
50) ________ is the assignment of jobs to work or processing centers.
Answer: View Answer
51) Suppose that a firm incurs a demand variance of 400 units per week,
and the variance of orders that it places equals 750 per week. What
is the value of the bullwhip measure for this company?
Answer: View Answer
52) Identify one advantage and one disadvantage of the doubling
approach over the formula approach to learning curve calculations.
Answer: View Answer
53) Identify three common occurrences that contribute to distortions of
information about what is really occurring in the supply chain.
Answer: View Answer
54) A graphic design studio is considering three new computers. The
first model, A, costs $5000. Model B and C cost $3000 and $1000
respectively. If each customer provides $50 of revenue and variable
costs are $20/customer, find the number of customers required for
each model to break even.
Answer: View Answer
55) Identify and describe three methods used for decision making under
conditions of uncertainty.
Answer: View Answer
56) The techniques for addressing the fixed-position layout are
complicated by what three factors? What is an alternative strategy
to address these?
Answer: View Answer
57) ________ reviews successful products for improvement during the
production process.
Answer: View Answer