1) Firms that are involved in more than one type of business could be evidence of an attempt to
a. increase private profit at the expense of consumers.
b. internalize some forms of positive externalities.
c. reduce the impact of government regulations on their business.
d. increase the private marginal cost of production.
Answer: View Answer
2) A streetlight is a
a. private good.
b. club good.
c. common resource.
d. public good.
Answer: View Answer
3) Private contracts between parties with mutual interests
a. will reduce the well-being of society.
b. will lead to market outcomes in which the public interest is sacrificed for personal gain.
c. can solve some inefficiencies associated with positive externalities.
d. will create negative externalities.
Answer: View Answer
4) State and local governments
a. use a mix of taxes and fees to generate revenue.
b. are required by federal mandate to levy income taxes.
c. are required to tax property at a standard rate set by the federal government.
d. cannot impose state excise taxes on products that are taxed by the federal government.
Answer: View Answer
5) Table 12-12
United States Income Tax Rates for a Single Individual, 2009 and
2009 Tax Rates Income Ranges 2010 Tax Rates Income Ranges
15% $0 $28,000 10% $0 $10,000
28% $28,000 $70,000 15% $10,000 $30,000
31% $70,000 $140,000 27% $30,000 $60,000
36% $140,000 $300,000 30% $60,000 $150,000
40% over $300,000 35% $150,000 $320,000
38% over $320,000
Refer to Table 12-12. Mia is a single person whose taxable income is $100,000 a year. What is her average tax rate in 2009?
a. 22.3%
b. 25.3%
c. 27.8%
d. 28.4%
Answer: View Answer
6) Which of the following equations is not valid?
a. Consumer surplus = Value to buyers – Amount paid by buyers
b. Producer surplus = Amount received by sellers – Cost to sellers
c. Total surplus = Value to buyers – Amount paid by buyers + Amount received by sellers – Costs of sellers
d. Total surplus = Value to sellers – Cost to sellers
Answer: View Answer
7) Total surplus
a. can be used to measure a markets efficiency.
b. is the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
c. is the to value to buyers minus the cost to sellers.
d. All of the above are correct.
Answer: View Answer
8) Which of the following statements is correct?
a. A general sales tax on food is regressive when low-income taxpayers spend a larger proportion of their income on food than high-income taxpayers.
b. A general sales tax on food is regressive when middle income taxpayers spend a smaller proportion of their income on food than high-income taxpayers.
c. A general sales tax on food is regressive when high-income taxpayers spend a larger proportion of their income on food than middle income taxpayers.
d. A general sales tax on food is regressive when high-income taxpayers spend a larger proportion of their income on food than low-income taxpayers.
Answer: View Answer
9) When a negative externality exists in a market, the cost to producers
a. is greater than the cost to society.
b. will be the same as the cost to society.
c. will be less than the cost to society.
d. will differ from the cost to society, regardless of whether an externality is present.
Answer: View Answer
10) Table 13-13
Output Total Cost
0 $40
10 $60
20 $90
30 $130
40 $180
50 $240
Refer to Table 13-13. What is average variable cost when output is 50 units?
a. $3.60
b. $4.00
c. $4.40
d. $4.80
Answer: View Answer
11) The deadweight loss from a tax of $8 per unit will be smallest in a market with
a. elastic demand and elastic supply.
b. elastic demand and inelastic supply.
c. inelastic demand and elastic supply.
d. inelastic demand and inelastic supply.
Answer: View Answer
12) When adding another unit of labor leads to an increase in output that is smaller than the increases in output that resulted from adding previous units of labor, the firm is experiencing
a. diminishing labor.
b. diminishing output.
c. diminishing marginal product.
d. negative marginal product.
Answer: View Answer
13) Which of the following events always would increase the size of the deadweight loss that arises from the tax on gasoline?
a. The demand for gasoline becomes more inelastic.
b. The slope of the supply curve for gasoline becomes steeper.
c. The amount of the tax per gallon of gasoline increases.
d. All of the above are correct.
Answer: View Answer
14) Which of the following policies is an example of a command-and-control policy?
a. subsidies to education
b. maximum levels of pollution that factories may emit
c. tradable pollution permits
d. None of the above is an example of a command-and-control policy.
Answer: View Answer
15)
Refer to Figure 14-12. If the figure in panel (a) reflects the long-run equilibrium of a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market, the figure in panel (b) most likely reflects
a. perfectly inelastic long-run market supply.
b. perfectly elastic long-run market supply.
c. the entry of firms into the industry when some resources used in production are available only in limited quantities.
d. the fact that zero profits cannot be sustained in the long run.
Answer: View Answer
16) Taxes on labor have the effect of encouraging
a. workers to work more hours.
b. the elderly to postpone retirement.
c. second earners within a family to take a job.
d. unscrupulous people to take part in the underground economy.
Answer: View Answer
17) On a 100-acre farm, a farmer is able to produce 3,000 bushels of wheat when he hires 2 workers. He is able to produce 4,400 bushels of wheat when he hires 3 workers. Which of the following possibilities is consistent with the property of diminishing marginal product?
a. The farmer is able to produce 5,600 bushels of wheat when he hires 4 workers.
b. The farmer is able to produce 5,400 bushels of wheat when he hires 4 workers.
c. The farmer is able to produce 5,200 bushels of wheat when he hires 4 workers.
d. Any of the above could be correct.
Answer: View Answer
18) Table 12-17
The dollar amounts in the last three columns are the taxes owed under the three different tax systems.
Income Tax System A Tax System B Tax System C
$100,000 $20,000 $20,000 $50,000
$250,000 $50,000 $75,000 $60,000
$500,000 $100,000 $210,000 $70,000
Refer to Table 12-17. Which of the three tax systems exhibits vertical equity?
a. Tax System A
b. Tax System B
c. Tax System C
d. All of the systems exhibit vertical equity.
Answer: View Answer
19) Total revenue minus only implicit costs is called
a. accounting profit.
b. economic profit.
c. opportunity cost.
d. None of the above is correct.
Answer: View Answer
20) Table 13-3
Number of Workers Output Fixed Cost Variable Cost Total Cost
0 0 $50 $0 $50
1 90 $50 $20 $70
2 170 $50 $40 $90
3 230 $50 $60 $110
4 240 $50 $80 $130
Refer to Table 13-3. The marginal product of the third worker is
a. 230 units.
b. 100 units.
c. 77 units.
d. 60 units.
Answer: View Answer
21) Table 13-1
Number of Workers Total Output Marginal Product
0 0 —
1 30
2 40
3 50
4 40
5 30
Refer to Table 13-1. What is total output when 4 workers are hired?
a. -10
b. 70
c. 120
d. 160
Answer: View Answer
22) Table 7-3
The only four consumers in a market have the following willingness to pay for a good:
Buyer Willingness to Pay
Carlos $15
Quilana $25
Wilbur $35
Ming-la $45
Refer to Table 7-3. If the price is $20, then consumer surplus in the market is
a. $20, and Wilbur and Ming-la purchase the good.
b. $45, and Carlos and Quilana purchase the good.
c. $45, and Quilana, Wilbur, and Ming-la purchase the good.
d. $55, and Carlos, Wilbur, and Ming-la purchase the good.
Answer: View Answer
23) 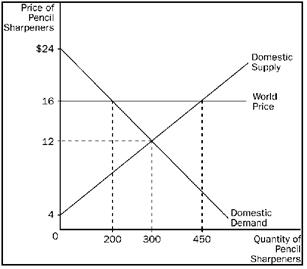
Refer to Figure 9-3. Relative to a no-trade situation, which of the following comes with trade?
a. Consumer surplus increases by $1,800 and producer surplus increases by $1,600.
b. Consumer surplus decreases by $1,000 and producer surplus increases by $1,500.
c. Consumer surplus decreases by $1,000 and producer surplus increases by $1,750.
d. Total surplus increases by $400.
Answer: View Answer
24) Scenario 13-1
Calvin wants to start his own business making candles. He can purchase a candle factory that costs $400,000. Calvin currently has $500,000 in the bank earning 3 percent interest per year.
Refer to Scenario 13-1. If Calvin purchases the factory with his own money, what is the annual implicit opportunity cost of purchasing the factory?
a. $0
b. $3,000
c. $12,000
d. $15,000
Answer: View Answer
25) On holiday weekends thousands of people picnic in state parks. Some picnic areas become so overcrowded the benefit or value of picnicking diminishes to zero. Suppose that the Minnesota State Park Service institutes a variable fee structure. On weekdays when the picnic areas get little use, the fee is zero. On normal weekends, the fee is $8 per person. On holiday weekends, the fee is $14 per person. The fee system corrects a problem known as the
a. Coase theorem.
b. free rider problem.
c. Tragedy of the Commons.
d. public goods problem.
Answer: View Answer
26) A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market is able to sell its product for $7. At its current level of output, the firm’s average total cost is $10. The firms marginal cost curve crosses its marginal revenue curve at an output level of 9 units. The firm experiences a
a. profit of more than $27.
b. profit of exactly $27.
c. loss of more than $27.
d. loss of exactly $27.
Answer: View Answer
27) The Doris Dairy Farm sells milk to a dairy broker in Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin. Because the market for milk is generally considered to be competitive, the Doris Dairy Farm does not choose the
a. quantity of milk to produce.
b. price at which it sells its milk.
c. profits it earns.
d. All of the above are correct.
Answer: View Answer
28) If the total cost curve gets steeper as output increases, the firm is experiencing
a. diseconomies of scale.
b. economies of scale.
c. diminishing marginal product.
d. increasing marginal product.
Answer: View Answer
29) A free rider is a person who
a. will only purchase a product on sale.
b. receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it.
c. can produce a good at no cost.
d. rides public transit regularly.
Answer: View Answer
30) 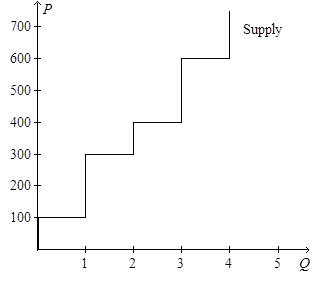
Refer to Figure 7-13. If the price of the good is $600, then
a. consumer surplus is $800.
b. consumer surplus is $900.
c. producer surplus is $900.
d. producer surplus is $1,000.
Answer: View Answer
31) Suppose a tax is imposed on the sellers of fast-food French fries. The burden of the tax will
a. fall entirely on the buyers of fast-food French fries.
b. fall entirely on the sellers of fast-food French fries.
c. be shared equally by the buyers and sellers of fast-food French fries.
d. be shared by the buyers and sellers of fast-food French fries but not necessarily equally.
Answer: View Answer
32) 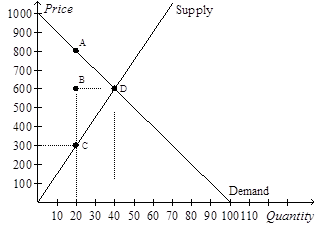
Refer to Figure 8-9. The consumer surplus without the tax is
a. $2,000.
b. $5,000.
c. $8,000.
d. $16,000.
Answer: View Answer
33) Sue earns income of $80,000 per year. Her average tax rate is 40 percent. Sue paid $4,500 in taxes on the first $30,000 she earned. What was the marginal tax rate on the rest of her income?
a. 15 percent
b. 32 percent
c. 40 percent
d. 55 percent
Answer: View Answer
34) Economists assume that the typical person who starts her own business does so with the intention of
a. donating the profits from her business to charity.
b. capturing the highest number of sales in her industry.
c. maximizing profits.
d. minimizing costs.
Answer: View Answer
35) Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Assuming that explicit costs are positive, economic profit is greater than accounting profit.
b. Assuming that implicit costs are positive, accounting profit is greater than economic profit.
c. Assuming that explicit costs are positive, accounting profit is equal to economic profit.
d. Assuming that implicit costs are positive, economic profit is positive.
Answer: View Answer
36) 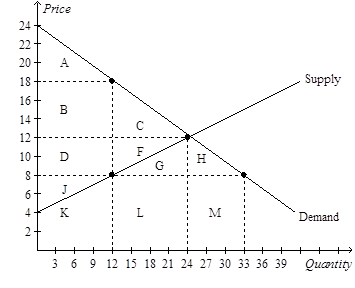
Refer to Figure 8-8. After the tax goes into effect, producer surplus is the area
a. D+F+G+H+J.
b. D+F+G+H.
c. D+F+J.
d. J.
Answer: View Answer
37) An example of an explicit cost would be the wages that a business owner pays her employees.
Answer: View Answer
38) The manager of a firm operating in a competitive market can ignore sunk costs when making business decisions.
Answer: View Answer
39) Consumer surplus is the amount a buyer actually has to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer is willing to pay for it.
Answer: View Answer
40) In some cases the government can make everyone better off by raising taxes to pay for certain goods that the market fails to provide.
Answer: View Answer
41) If Darby values a soccer ball at $50, and she pays $40 for it, her consumer surplus is $90.
Answer: View Answer
42) Diminishing marginal product exists when the total cost curve becomes horizontal as outputs increases.
Answer: View Answer
43) If the marginal cost of producing the fifth unit of output is higher than the marginal cost of producing the fourth unit of output, then at five units of output, average total cost must be rising.
Answer: View Answer
44) If Darby values a soccer ball at $50, and she pays $40 for it, her consumer surplus is $10.
Answer: View Answer