Average fixed cost is defined as
A) total variable cost divided by quantity.
B) quantity divided by total variable cost.
C) the change in total variable cost divided by the change in quantity.
D) total fixed cost divided by quantity.
A) total variable cost divided by quantity.
B) quantity divided by total variable cost.
C) the change in total variable cost divided by the change in quantity.
D) total fixed cost divided by quantity.
Answer:View Answer
| 1974 | 2011 | |
| Minimum wage per hour | $ 2.00 | $ 7.25 |
| Weekly income from minimum wage | $80.00 | $290.00 |
| Cost of a standard basket of goods | $47.00 | $225.00 |
| Number of baskets per week | 1.70 | 1.29 |
Table 2.5
By what percentage did the federal minimum wage increase from 1974 to 2011?
A) 72.41%
B) 262.5%
C) 362.5%
D) 525.0%
Answer:View Answer
For the perfectly competitive firm
A) price always equals average cost.
B) price always equals marginal cost.
C) price always equals marginal revenue.
D) price always equals average variable cost.
A) price always equals average cost.
B) price always equals marginal cost.
C) price always equals marginal revenue.
D) price always equals average variable cost.
Answer:View Answer
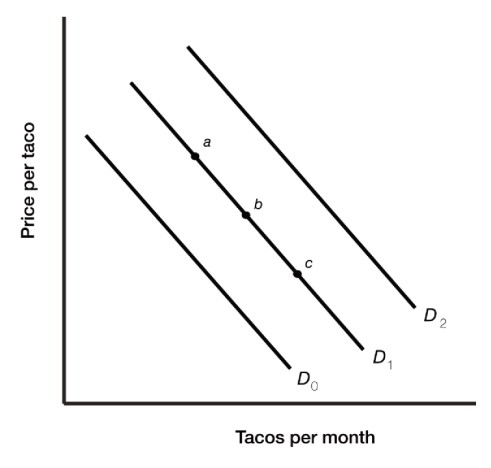
Figure 3.3
Figure 3.3 illustrates the demand for tacos. An increase in price of tacos would bring about a movement from
A) point a to point c.
B) point c to point a.
C) D2 to D0.
D) D0 to D1.
Answer:View Answer
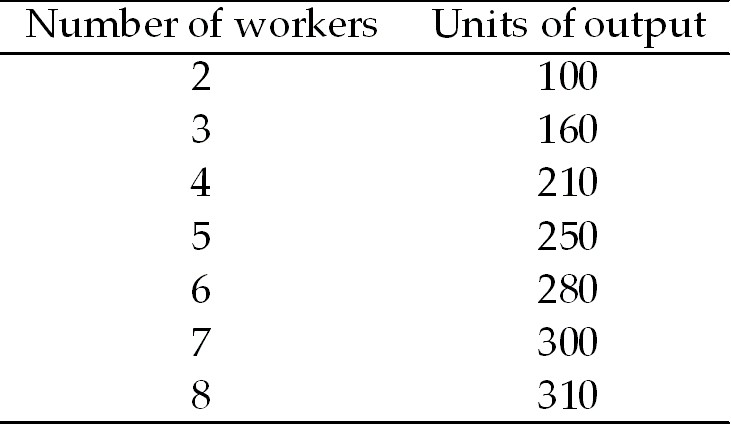 Table 10.1
Table 10.1Suppose that this year the wage rate is $30 and the price of the good is $1. If the firm is maximizing profit ________ workers will be hired. Next year the wage rate will increase to $40, but the price of the good will remain at $1. Then ________ workers will be hired.
A) 6; 5
B) 6; 6
C) 7; 6
D) 5; 5
Answer:View Answer
Compared to a pollution tax, a policy of uniform abatement with permits is
A) less efficient.
B) more efficient.
C) exactly as efficient.
D) either more or less efficient depending on the number of firms affected.
A) less efficient.
B) more efficient.
C) exactly as efficient.
D) either more or less efficient depending on the number of firms affected.
Answer:View Answer
When economies of scale are present, but sufficiently large to generate a natural monopoly, the expected market structure is
A) monopoly.
B) monopolistic competition.
C) perfect competition.
D) oligopoly.
A) monopoly.
B) monopolistic competition.
C) perfect competition.
D) oligopoly.
Answer:View Answer
Which of the following is NOT an example of a consumption expenditure?
A) a digital camera you purchase to take on vacation
B) a new county jail
C) a motorcycle you purchase to ride on the weekends
D) a restaurant meal
A) a digital camera you purchase to take on vacation
B) a new county jail
C) a motorcycle you purchase to ride on the weekends
D) a restaurant meal
Answer:View Answer
Which of the following best characterizes the tradeoff faced by a monopolist when deciding what quantity to produce?
A) The firm can increase its output, but needs to lower its price for only the marginal unit of output.
B) The firm can increase its output, but to do so it must charge a higher price to all customers.
C) The firm gets more revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets less revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.
D) The firm gets less revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets more revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.
A) The firm can increase its output, but needs to lower its price for only the marginal unit of output.
B) The firm can increase its output, but to do so it must charge a higher price to all customers.
C) The firm gets more revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets less revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.
D) The firm gets less revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets more revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.
Answer:View Answer
Blu-ray disc players, iPhones, and hybrid cars are generally considered to be ________ goods.
A) durable
B) nondurable
C) intermediate
D) service
A) durable
B) nondurable
C) intermediate
D) service
Answer:View Answer
Costs increase with output in an increasing-cost industry because
A) input prices increase as the industry competes for scarce resources.
B) firms may be forced to use less productive inputs.
C) the firms become monopolies.
D) Both A and B are correct.
A) input prices increase as the industry competes for scarce resources.
B) firms may be forced to use less productive inputs.
C) the firms become monopolies.
D) Both A and B are correct.
Answer:View Answer
The biggest problem caused by a deflation is that
A) prices fall.
B) wages fall.
C) people cannot repay their debts.
D) interest rates rise.
A) prices fall.
B) wages fall.
C) people cannot repay their debts.
D) interest rates rise.
Answer:View Answer
Quantity of Frozen Latte-On-A-Stick Supplied
| Price | Flo’s Supply | Rita’s Supply |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 | 6 |
| 4 | 9 | 9 |
| 5 | 15 | 12 |
Table 3.1
Which shows Flo’s and Rita’s individual supply schedules for frozen latte-on-a-stick. Assuming Flo and Rita are the only suppliers in the market, what is the market quantity supplied at a price of $2?
A) 0
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
Answer:View Answer
An arrangement between firms whereby decision-making is controlled by a board of trustees is known as
A) a trust.
B) a compact between industry and government.
C) predatory pricing.
D) a merger.
A) a trust.
B) a compact between industry and government.
C) predatory pricing.
D) a merger.
Answer:View Answer
| Number of Figs | VC | MC | AVC | FC | TC | ATC |
| 0 | 100 | |||||
| 1 | 90 | 90 | ||||
| 2 | 135 | |||||
| 3 | 80 | |||||
| 4 | 400 |
Table 5.4
Table 5.4 presents the cost schedule for David’s Figs. If David produces two figs, David’s average variable costs are
A) $80.
B) $85.
C) $90.
D) $170.
Answer:View Answer
A period in which real GDP in the economy declines for at least six months is referred to as
A) long term growth.
B) a recession.
C) a positive fluctuation.
D) living standards.
A) long term growth.
B) a recession.
C) a positive fluctuation.
D) living standards.
Answer:View Answer
What happens to your purchasing power if inflation is less than you anticipated?
A) It decreases.
B) It increases.
C) It devalues your net worth.
D) It won’t change much.
A) It decreases.
B) It increases.
C) It devalues your net worth.
D) It won’t change much.
Answer:View Answer
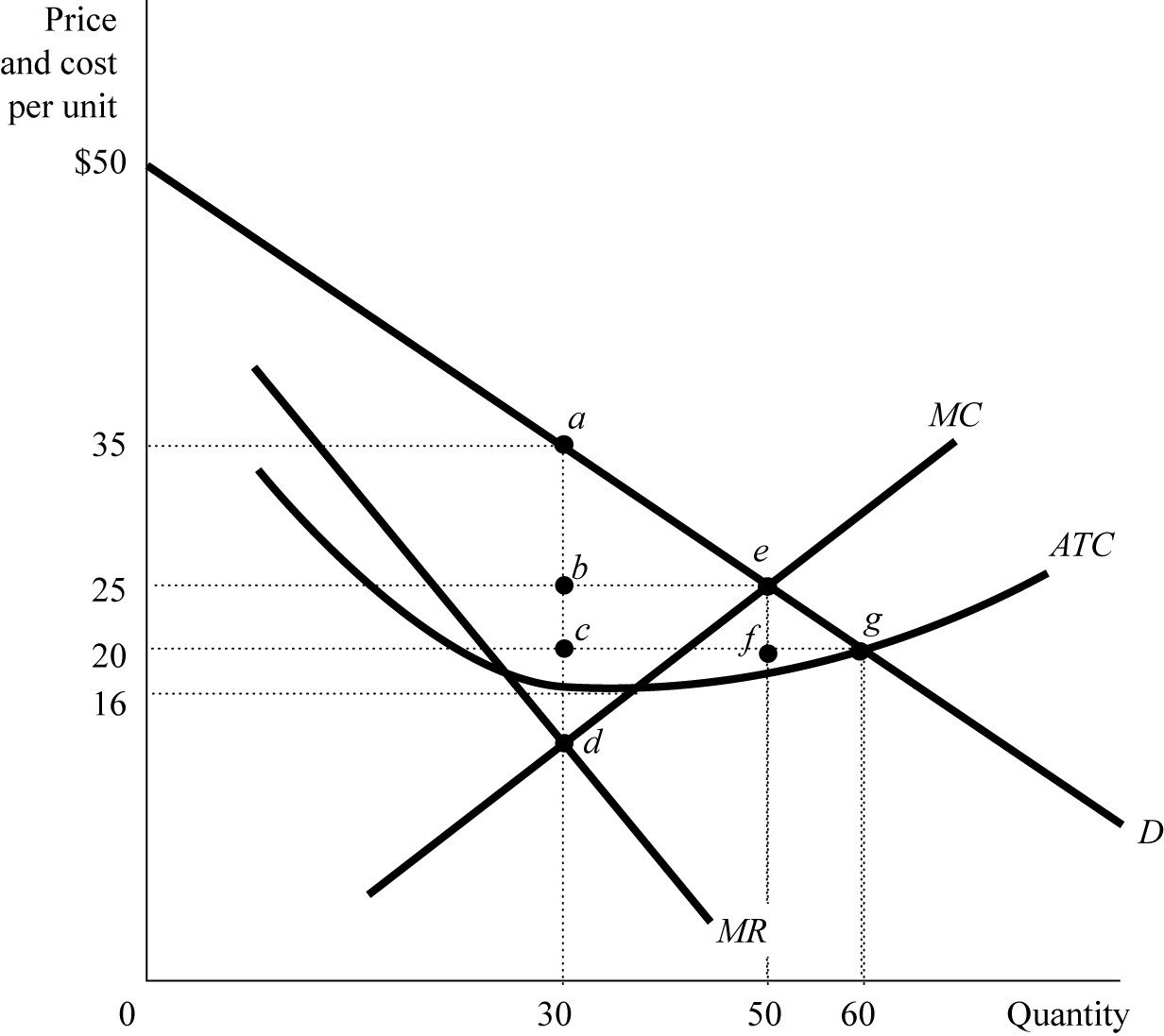 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Figure 7.4 shows a monopolist’s demand curve, marginal revenue, and its costs. The monopolist would maximize its profit by charging a price of
A) $35.
B) $25.
C) $20.
D) $16.
Answer:View Answer
If the quantity demanded of restaurant meals increases by 20% when income increases by 10%, the demand for restaurant meals is
A) price sensitive.
B) income-inelastic.
C) income-elastic.
D) price insensitive.
A) price sensitive.
B) income-inelastic.
C) income-elastic.
D) price insensitive.
Answer:View Answer