1) The rate is constant over time.
Answer: View Answer
2) Buffered solution 1 has a greater buffering capacity than buffered
solution 2 .
Answer: View Answer
3) Steel is a substitutional alloy.
Answer: View Answer
4) Ice is a molecular solid.
Answer: View Answer
5) Draw a molecular orbital diagram for O2 and N2. Using molecular
orbital theory, explain why the removal of one electron in O2
strengthens bonding, while the removal of one electron in N2
weakens bonding.
Answer: View Answer
6) Ionization energy increases with an increasing number of electrons.
Answer: View Answer
7) When a system performs work on the surroundings, the work is
reported with a negative sign.
Answer: View Answer
8) The diffusion of a gas is faster than the effusion of a gas.
Answer: View Answer
9) Would you predict an increase or decrease in entropy for each of
the following?: 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g)
Answer: View Answer
10) A state function does not depend on the system’s past or future.
Answer: View Answer
11) Which of the following is not a postulate of the kinetic molecular
theory?
A) Gas particles have most of their mass concentrated in the
nucleus of the atom
B) The moving particles undergo perfectly elastic collisions with
the walls of the container
C) The forces of attraction and repulsion between the particles are
insignificant
D) The average kinetic energy of the particles is directly
proportional to the absolute temperature
E) All of the above are postulates of the kinetic molecular theory
Answer: View Answer
12) Phosphorus is found in nature
A) as white phosphorus
B) as red phosphorus
C) as black phosphorus
D) usually as the PO43 ion in phosphate rock
E) in gypsum
Answer: View Answer
13) The two salts AgX and AgY exhibit very similar solubilities in
water. It is known that the salt AgX is much more soluble in acid
than is AgY. What can be said about the relative strengths of the
acids HX and HY?
A) Nothing
B) HY is stronger than HX
C) HX is stronger than HY
D) The acids are weak acids and have equal values for Ka
E) Both acids are strong
Answer: View Answer
14) Which of the following is true for a buffered solution?
A) The solution resists change in its [H+]
B) The solution will not change its pH very much even if a
concentrated acid is added
C) The solution will not change its pH very much even if a strong
base is added
D) Any H+ ions will react with a conjugate base of a weak acid
already in solution
E) All of these
Answer: View Answer
15) The molar solubility of PbI2 is 52103M. Calculate the value of Ksp
for PbI2.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
16) Consider the following hypothetical reaction (at 307.8 K). Standard
free energies in kJ/mol are given in parentheses.
A ![]() B + C DG =
B + C DG =
?
(-32.2) (207.8) (-237.0)
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 8
K?
A) 0.31
B) 1.0
C) 9.0 104
D) 273
E) 0.43
Answer: View Answer
17) Solid calcium hydroxide is dissolved in water until the pH of the
solution is 11.44. The hydroxide ion concentration [OH] of the
solution is:
A) 3.6 1012 M
B) 5.5 103 M
C) 2.8 103 M
D) 1.4 103 M
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
18) A solution of water and a nonvolatile, nonionizing compound is
placed in a tube with a semipermeable membrane on one side. The
tube is placed in a beaker of pure water. What initial net effect
will occur?
A) Water will flow from the beaker to the tube
B) Water will flow from the tube to the beaker
C) The compound will pass through the membrane into the
solution
D) Nothing will move through the membrane either way
E) Equilibrium is immediately established
Answer: View Answer
19) The pH at the equivalence point of the titration of a strong acid
with a strong base is:
A) 3.9
B) 4.5
C) 7.0
D) 8.2
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
20) A metal crystallizes with a face-centered cubic lattice. The edge
of the unit cell is 395 pm. The diameter of the metal atom is:
A) 140 pm
B) 198 pm
C) 279 pm
D) 395 pm
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
21) The first electron affinity value for oxygen is _______ and the
second electron affinity value is ________.
A) unfavorable (endothermic), favorable (exothermic)
B) unfavorable (endothermic), unfavorable (endothermic)
C) favorable (exothermic), favorable (exothermic)
D) favorable (exothermic), unfavorable (endothermic)
E) More information is needed.
Answer: View Answer
22) The geometry of a coordination compound with a coordination number
of 4 is
A) tetrahedral, in order to minimize repulsions between the
ligands
B) octahedral, since there are two different positions possible for
each ligand
C) square planar, to allow room for the counterion because the
ligands take up so much space
D) linear, since there are two ligands on each side of the
transition metal
E) tetrahedral or square planar, but too difficult to predict based
on the information given
Answer: View Answer
23) A solution containing 10.mmol of ![]() and 0mmol
and 0mmol
of ![]() is
is
titrated with 1.7M HCl. What total volume of HCl must be added to
reach the second equivalence point?
A) 8.8 mL
B) 5.9 mL
C) 2.9 mL
D) 14.7 mL
E) 19.7 mL
Answer: View Answer
24) All of the following statements about the greenhouse effect are
true except:
A) It occurs only on earth
B) The molecules H2O and CO2 play an important role in retaining
the atmosphere’s heat
C) Low humidity allows efficient radiation of heat back into
space
D) The carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere is quite stable
E) A and D
Answer: View Answer
25) In the Lewis structure for ICl2, how many lone pairs of electrons
are around the central iodine atom?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
Answer: View Answer
26) Which of the following pairs is incorrect?
A) iodine trichloride, ICl3
B) phosphorus pentoxide, P2O5
C) ammonia, NH3
D) sulfur hexafluoride, SF6
E) All of the above pairs are correct.
Answer: View Answer
27) In 1928, 29.3 g of a new element was isolated from 660 kg of the
ore molybdenite. The percent by mass of this element in the ore
was:
A) 44 %
B) 6.6 %
C) 29.3 %
D) 0.0044 %
E) 19.3 %
Answer: View Answer
28) 10mL of 0.50 M HCl is added to a 100.-mL sample of 0.456M HNO2 (Ka
for HNO2=4.0104). What is the equilibrium concentration of NO2
ions?
A) 2.4 103 M
B) 1.6 104 M
C) 4.0 101 M
D) 4.9 102 M
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
29) A concentration cell is constructed using two Ni electrodes with
Ni2+ concentrations of 1.0 M and 1.00 104M in the two half-cells.
The reduction potential of Ni2+ is 0.23 V. Calculate the potential
of the cell at 25C.
A) 0.368 V
B) +0.132 V
C) 0.132 V
D) +0.118 V
E) +0.0592 V
Answer: View Answer
30) The Haber process
A) is used to manufacture ammonia
B) transforms nitrogen to other nitrogen-containing compounds
C) is used to recover sulfur from underground deposits
D) is used to produce nitric acid
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
31) wPCl5 + xH2O yPOCl3 + zHCl
The above equation is properly balanced when:
A) w = 1, x = 2, y = 2, z = 4
B) w = 2, x = 2, y = 2, z = 2
C) w = 2, x = 2, y = 2, z = 1
D) w = 1, x = 1, y = 1, z = 2
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
32) For the reaction H2O(l) H2O(g) at 298 K and 1.0 atm, DH is more
positive than DE by 2.5 kJ/mol. This quantity of energy can be
considered to be
A) the heat flow required to maintain a constant temperature
B) the work done in pushing back the atmosphere
C) the difference in the HO bond energy in H2O(l) compared to
H2O(g)
D) the value of DH itself
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
33) Which of the following is true?
A) The first ionization energy for Zn is significantly higher than
that of Sc
B) The first ionization energy for Zn is significantly lower than
that of Sc
C) The third ionization energy for Zn is significantly higher than
that of Sc
D) The third ionization energy for Zn is significantly lower than
that of Sc
E) Two of these are correct
Answer: View Answer
34) Electrolysis of a molten salt with the formula MCl, using a current
of 3.86 amp for 16.2 min, deposits 1.52 g of metal. Identify the
metal. (1faraday=96,485coulombs)
A) Li
B) Na
C) K
D) Rb
E) Ca
Answer: View Answer
35) Calculate the pOH of a 0.12 M solution of acetic acid
(Ka=1.8105).
A) 2.83
B) 8.33
C) 5.67
D) 11.17
E) 1.91
Answer: View Answer
36) The chemistry of silicon is dominated by its bonding with
A) Cl
B) S
C) Al
D) F
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
37) Which of the following statements from Dalton’s atomic theory is no
longer true, according to modern atomic theory?
A) Elements are made up of tiny particles called atoms
B) Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions
C) All atoms of a given element are identical
D) Atoms are indivisible in chemical reactions
E) All of these statements are true according to modern atomic
theory
Answer: View Answer
38) Which of the following molecules exhibits chirality?
A) CH4
B) CH3OH
C) CH3CH2OH
D) 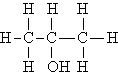
E) none of these
Answer: View Answer
39) Which of the following do you need to know to be able to calculate
the molarity of a salt solution?
I. the mass of salt added
II. the molar mass of the salt
III. the volume of water added
IV. the total volume of the solution
A) I, III
B) I, II, III
C) II, III
D) I, II, IV
E) You need all of the information.
Answer: View Answer
40) Nitroglycerin, the main component of dynamite, decomposes very
rapidly and exothermically according to the equation:
4C3H5N3O9(l) 6N2(g) + 12CO2(g) + 10H2O(g) + O2(g) + energy
What is the total volume of products that would be produced
from 595 g of nitroglycerin? Assume the heat released caused the
temperature to become 233C and the pressure to be 10.0 atm.
A) 36.3 L
B) 78.9 L
C) 16.3 L
D) 58.7 L
E) 93.9 L
Answer: View Answer
41) You have 75.0mL of a 2.50M solution of Na2CrO4(aq). You also have
125mL of a 1.88M solution of AgNO3(aq). Calculate the concentration
of NO3 after the two solutions are mixed together.
A) 0.00 M
B) 0.588 M
C) 1.18 M
D) 2.35 M
E) 4.50 M
Answer: View Answer
42) Given the following data, calculate the normal boiling point for
formic acid (HCOOH).
| DHf(kJ/mol) | S(J/mol K) | |
| HCOOH(l) | -410. | 130.0 |
| HCOOH(g) | -363 | 251.1 |
A) 0.39 C
B) 388 C
C) 661 C
D) 279 C
E) 115 C
Answer: View Answer
43) At a given temperature, K=0.017 for the equilibrium:
PCl5(g)![]() PCl3(g)+Cl2(g)
PCl3(g)+Cl2(g)
What is K for:
Cl2(g)+PCl3(g)![]() PCl5(g)?
PCl5(g)?
A) 0.017
B) 59
C) 0.00029
D) 17
E) 3500
Answer: View Answer
44) Name the following compounds: K2Cr2O7
Answer: View Answer
45) In a(n) __________ alloy some of the host metal atoms are replaced
by other metal atoms of similar size.
Answer: View Answer
46) Which of the following ligands are capable of linkage
isomerism?
| N |
| NO2 |
| NH3 |
| NH2CH2CH2NH2 |
| OCN |
| Cl |
| H2O |
| SCN |
Answer: View Answer
47) Indicate the total number of isomers in the following compound:
C4H10
Answer: View Answer
48) Write the electron configuration for the following: I
Answer: View Answer