1) What is the quality loss function (QLF)?
Answer: View Answer
2) Linear programming helps operations managers make decisions
necessary to make effective use of resources such as machinery,
labor, money, time, and raw materials.
Answer: View Answer
3) Earliest due date is a shop floor dispatching (sequencing) rule
that relates the time available to complete a job to the amount of
work left to be completed.
Answer: View Answer
4) How can global operations improve the supply chain?
Answer: View Answer
5) In the production order quantity (POQ) model, inventory does not
arrive in a single moment but flows in at a steady rate, resulting
in a larger production/order quantity than in an otherwise
identical EOQ problem.
Answer: View Answer
6) ________ uses computerized short-term scheduling to overcome the
disadvantages of rule-based systems by providing the user with
interactive computing and graphical output.
Answer: View Answer
7) P(: 0.05 + (1 – 0.05)0.102= 0.05 + (0.95)(0.01) = 0.0595
EMV(1 supplier) = $12,000(1 – 0.145) + $112,000(0.145) = $10,260 +
$16,240 = $26,500
EMV(2 suppliers) = $24,000(1 – 0.0595) + $124,000(0.0595) = $22,572
+ $7,378 = $29,950
Answer: View Answer
8) If 100 units of Q are needed and 10 are already in stock, then the
gross requirement is 100 and the net requirement is 90.
Answer: View Answer
9) Category management is the use of computer software to evaluate the
profitability of various merchandising plans for hundreds of
categories.
Answer: View Answer
10) A company is deciding where to assign its summer intern. The
manager estimates that the intern can save $10,000 in the supply
chain or increase sales (revenue) by $25,000. If sales (revenue) is
divided into the three categories shown in the table, where should
the manager assign the intern to maximize profits?
| Supply Chain Costs | Production Costs | Profits | |
| % of current sales (revenue) | 35 | 25 | 40 |
Answer: View Answer
11) Gantt charts give a timeline for each of a project’s activities,
but they do not adequately illustrate the interrelationships
between the activities and the resources.
Answer: View Answer
12) One use of camera-and-computer-based vision systems is to replace
humans doing tedious and error-prone visual inspection activities.
Answer: View Answer
13) Manufacturers may want to locate close to their customers if the
transportation of finished goods is expensive or difficult.
Answer: View Answer
14) A firm has modeled its experience with industrial accidents and
found that the number of accidents per year (y-hat) is related to
the number of employees (x) by the regression equation:
y-hat = 3.3 + 0.049x. The r-squared value is 0.68. The regression
is based on 20 annual observations. The firm intends to employ 480
workers next year. How many accidents do you project? How much
confidence do you have in that forecast?
Answer: View Answer
15) Linear programming is an appropriate problem-solving technique for
decisions that have no alternative courses of action.
Answer: View Answer
16) Forecasts of individual products tend to be more accurate than
forecasts of product families.
Answer: View Answer
17) A hotel room that goes unrented and an airline seat that goes
unsold are both examples of perishable inventory in services.
Answer: View Answer
18) A product is currently made in a process-focused shop, where fixed
costs are $9,000 per year and variable costs are $50 per unit. The
firm is considering a fundamental shift in process, to repetitive
manufacturing. The new process would have fixed costs of $90,000,
and variable costs of $5. What is the crossover point for these
processes? For what range of outputs is each process appropriate?
Answer: View Answer
19) The first unit of a product took 50 hours to build, and the
learning curve is 80%. How long will it take to make the third
unit? (Use at least three decimals in the exponent if you use the
formula approach.)
A) under 30 hours
B) about 32 hours
C) about 35 hours
D) about 50 hours
E) about 75 hours
Answer: View Answer
20) An assembly line consists of 21 tasks grouped into 5 workstations.
The sum of the 21 task times is 85 minutes. The largest assigned
cycle time is 20 minutes. What is the efficiency of this line?
A) 4.2 percent
B) 17 percent
C) 85 percent
D) 100 percent
E) 21 percent
Answer: View Answer
21) When the number of shipments in a feasible solution is less than
the number of rows plus the number of columns minus one:
A) the solution is optimal
B) a dummy source must be created
C) a dummy destination must be created
D) there is degeneracy, and an artificial allocation must be
created
E) the closed path has a triangular shape
Answer: View Answer
22) A two-component process has an 81% success rate in series and a 99%
success rate in parallel. If each component has the same
reliability, what is the reliability of an individual
component?
A) 50%
B) 90%
C) 99%
D) 18%
E) 81%
Answer: View Answer
23) Which of the following is FALSE regarding repetitive processes?
A) They use modules
B) They allow easy switching from one product to the other
C) They are the classic assembly lines
D) They have more structure and less flexibility than a job shop
layout
E) They include the assembly of basically all automobiles
Answer: View Answer
24) The analysis tool that lists products in descending order of their
individual dollar contribution to the firm is:
A) decision tree analysis
B) Pareto analysis
C) breakeven analysis
D) product-by-value analysis
E) product life cycle analysis
Answer: View Answer
25) For the problem below, what is the quantity assigned to the cell
Source 1-Destination 2 using the intuitive method for an initial
feasible solution?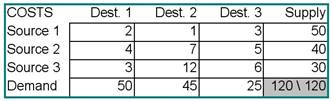
A) 1
B) 5
C) 30
D) 45
E) 50
Answer: View Answer
26) A manufacturing company preparing to build a new plant is
considering three potential locations for it. The fixed and
variable costs for the three alternative locations are presented
below.
a. Complete a numeric locational cost-volume analysis.
b. Indicate over what range each of the alternatives A, B, C is the
low-cost choice.
c. Is any alternative never preferred? Explain.
| Costs | A | B | C |
| Fixed ($) | 2,500,000 | 2,000,000 | 3,500,000 |
| Variable ($ per unit) | 21 | 25 | 15 |
Answer: View Answer
27) Which of the following is NOT an advantage of level scheduling?
A) stable employment
B) lower absenteeism
C) matching production exactly with sales
D) lower turnover
E) more employee commitment
Answer: View Answer
28) Which of the following values of alpha would cause exponential
smoothing to respond the SLOWEST to forecast errors?
A) 0.10
B) 0.2246
C) 0.50
D) 0.90
E) cannot be determined
Answer: View Answer
29) A manager wishes to build a 3-sigma range chart for a process. The
sample size is five, the mean of sample means is 16.01, and the
average range is 5.3. From Table S6.1, the appropriate value of
D3is 0, and D4is 2.115. What are the UCL and LCL, respectively, for
this range chart?
A) 33.9 and 11.2
B) 33.9 and 0
C) 11.2 and 0
D) 6.3 and 0
E) 31.91 and 0.11
Answer: View Answer
30) Labor standards can help to determine which of the following?
A) labor content of a product
B) staffing needs
C) incentive plans
D) efficiency
E) all of the above
Answer: View Answer
31) One use of short-range forecasts is to determine:
A) planning for new products
B) capital expenditures
C) research and development plans
D) facility location
E) job assignments
Answer: View Answer
32) A difference between minimization and maximization problems is
that:
A) minimization problems cannot be solved with the corner-point
method
B) maximization problems often have unbounded regions
C) minimization problems often have unbounded regions
D) minimization problems cannot have shadow prices
E) minimization problems are more difficult to solve than
maximization problems
Answer: View Answer
33) Which one of the following is NOT a layout tactic in a JIT
environment?
A) work cells for families of products
B) fixed equipment
C) minimizing distance
D) little space for inventory
E) poka-yoke devices
Answer: View Answer
34) In assembly-line balancing, cycle time (the ratio of available
production time to scheduled production) is the:
A) minimum time that a product is allowed at each workstation
B) maximum time that a product is allowed at each workstation
C) inverse of the minimum number of workstations needed
D) sum of all the task times divided by the maximum number of
workstations
E) equivalent of the maximum task time among all tasks
Answer: View Answer
35) Rienzi Farms grows sugar cane and soybeans on its 500 acres of
land. An acre of soybeans brings a $1000 contribution to overhead
and profit; an acre of sugar cane has a contribution of $2000.
Because of a government program no more than 200 acres may be
planted in soybeans. During the planting season 1200 hours of
planting time will be available. Each acre of soybeans requires 2
hours, while each acre of sugar cane requires 5 hours. The company
seeks maximum contribution (profit) from its planting decision.
a. Formulate the problem as a linear program.
b. Solve using the corner-point method.
Answer: View Answer
36) The c-chart signals whether there has been a:
A) gain or loss in uniformity
B) change in the number of defects per unit
C) change in the central tendency of the process output
D) change in the percent defective in a sample
E) change in the AOQ
Answer: View Answer
37) Which one of the following courses of actions would NOT be taken by
a firm wanting to pursue a learning curve steeper than the industry
average?
A) following an aggressive pricing policy
B) focusing on continuing cost reduction
C) keeping capacity equal to demand to control costs
D) focusing on productivity improvement
E) building on shared experience
Answer: View Answer
38) A toy manufacturer makes its own wind-up motors, which are then put
into its toys. While the toy manufacturing process is continuous,
the motors are intermittent flow. Data on the manufacture of the
motors appears below.
Annual demand (D) = 50,000 units Daily subassembly production rate
= 1,000
Setup cost (S) = $85 per batch Daily subassembly usage rate =
200
Carrying cost = $.20 per unit per year
(a) To minimize cost, how large should each batch of subassemblies
be?
(b) Approximately how many days are required to produce a
batch?
(c) How long is a complete cycle?
(d) What is the average inventory for this problem?
(e) What is the total annual inventory cost (holding plus setup) of
the optimal behavior in this problem?
Answer: View Answer
39) The ability of an organization to produce goods or services that
have some uniqueness in their characteristics is:
A) mass production
B) time-based competition
C) competing on productivity
D) competing on quality
E) competing on differentiation
Answer: View Answer
40) A firm operates a flow shop building kitchen cabinetry for
recreational vehicles. The major activities of this process are
listed below.
| Task | Duration (hours) | Predecessor 1 | Predecessor 2 | Predecessor 4 |
| A | 4 | — | ||
| B | 6 | — | ||
| C | 2 | A | ||
| D | 6 | A | ||
| E | 3 | B | C | |
| F | 3 | B | C | |
| G | 5 | D | E | F |
| H | 1 | G |
a. Draw the appropriate network for this project.
b. What would the cycle time be if the goal is to produce 20 units
per month (the plant operates
160 hours per month)?
c. What is the theoretical minimum number of workstations
needed?
d. Balance with the most following tasks heuristic. What tasks are
assigned to which stations?
e. What is the efficiency of the line obtained in part d?
Answer: View Answer
41) A firm practices a pure chase strategy. Production last quarter was
Demand over the next four quarters is estimated to be 900, 700,
1000, and 1000. Hiring cost is $20 per unit, and layoff cost is $5
per unit. Over the next year, what will be the sum of hiring and
layoff costs?
A) $500
B) $2,500
C) $7,500
D) $7,000
E) $12,500
Answer: View Answer
42) Which of the following is NOT one of the four main types of
inventory?
A) raw material inventory
B) work-in-process inventory
C) maintenance/repair/operating supply inventory
D) safety stock inventory
E) finished-goods inventory
Answer: View Answer
43) Consider the network described in the table below.
| Activity |
Immediate Predecessor(s) |
Pessimistic | Probable | Optimistic |
| J | — | 15 | 10 | 8 |
| K | — | 9 | 8 | 7 |
| L | J | 10 | 6 | 5 |
| M | J | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| N | K,M | 9 | 5 | 1 |
| O | K,M | 10 | 7 | 4 |
| P | L,N | 10 | 8 | 3 |
a. Calculate the expected duration of each activity.
b. Calculate the expected duration and variance of the critical
path.
c. Calculate the probability that the project will be completed in
fewer than 30 time units.
Answer: View Answer
44) Which of the following is NOT a limitation of PERT?
A) Project activities have to be clearly defined, independent, and
stable in their relationships
B) Precedence relationships must be specified and networked
together
C) Only one time estimate can be used for each activity
D) Time estimates tend to be subjective and are subject to fudging
by managers
E) There is the inherent danger of placing too much emphasis on the
critical path
Answer: View Answer
45) At Hard Rock Caf, tasks that reflect operations or operations
management include:
A) designing efficient layouts
B) providing meals
C) receiving ingredients
D) preparing effective employee schedules
E) all of the above
Answer: View Answer
46) The usual purpose of an R-chart is to signal whether there has been
a:
A) gain or loss in dispersion
B) change in the percent defective in a sample
C) change in the central tendency of the process output
D) change in the number of defects in a sample
E) change in the consumer’s risk
Answer: View Answer
47) A simple CPM network has five activities, A, B, C, D, and E. A is
an immediate predecessor of C and of D. B is also an immediate
predecessor of C and of D. C and D are both immediate predecessors
of E. Which of the following statements is true?
A) There are two paths in this network
B) There are four paths in this network
C) There are five paths in this network
D) There are 25 paths in this network
E) There are six paths in this network
Answer: View Answer
48) When a set of jobs must pass through two workstations whose
sequence is fixed, ________ is the sequencing rule most commonly
applied.
A) critical ratio
B) earliest due date
C) first come, first served
D) slack time remaining
E) Johnson’s rule
Answer: View Answer
49) Resources held by the public are also said to be held in what?
A) escrow
B) the system
C) contempt
D) perpetuity
E) the common
Answer: View Answer
50) Process X has fixed costs of $10,000 and variable costs of $2.40
per unit. Process Y has fixed costs of $9,000 and variable costs of
$2.25 per unit. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The crossover point is approximately 6667 units
B) It is impossible for one process to have both of its costs lower
than those of another process
C) Process Y is cheaper than process X at all volumes
D) Process X should be selected for very large production
volumes
E) Process X is more profitable than process Y and should be
selected
Answer: View Answer
51) The smaller the percentage established for allowances:
A) the closer is normal time to standard time
B) the closer is average observed time to normal time
C) the larger is the performance rating factor
D) the larger is the required sample size
E) the larger is the number of observations in the work sampling
Answer: View Answer
52) Which of the following best describes Vizio’s sourcing
strategy?
A) few suppliers
B) keiretsu
C) joint venture
D) vertical integration
E) virtual company
Answer: View Answer
53) The average observed time for a given job is 10 minutes. The
performance rating is 80%, and allowances are set by contract at
10%. What is the standard time?
A) 8.80 minutes
B) 8.88 minutes
C) 10.00 minutes
D) 19.00 minutes
E) 19.80 minutes
Answer: View Answer
54) What value of the bullwhip measure would indicate that a dampening
scenario exists?
A) greater than 1
B) greater than 0
C) less than 0
D) less than 1
E) 0
Answer: View Answer
55) Ethical issues that may arise in projects large and small
include:
A) gifts from contractors
B) exaggerated expense reports
C) compromised quality standards to meet bonuses or avoid penalties
related to schedules
D) pressure to mask delays with false status reports
E) all of the above
Answer: View Answer
56) A(n) ________ involves timing a sample of a worker’s performance
and using it as a basis for setting a standard time.
Answer: View Answer
57) What are predetermined time standards?
Answer: View Answer
58) The mean and standard deviations for a process are = 90 and = 9,
respectively. For the variable control chart, a sample size of 16
will be used. Calculate the standard deviation of the sample means.
Answer: View Answer
59) Weekly usage of a product is 8 units. Since the plant operates 50
weeks per year, this leads to annual usage of 400 units. Setup cost
is $40 and annualized carrying cost is $80. Weekly production of
this product is 12 units. Lead time is four weeks, and safety stock
is one week’s production. What is optimal kanban size? What is the
optimal number of kanbans?
Answer: View Answer
60) A waiting line meeting the M/M/1 assumptions has an arrival rate of
4 per hour and a service rate of 12 per hour. What is the
probability that the waiting line is empty?
Answer: View Answer
61) A(n) ________ queuing system has one waiting line, but several
servers; a(n) ________ queuing system is one in which the customer
receives services from several stations before exiting the system
Answer: View Answer