1)(Last Word) The post hoc fallacy and the correlation problem both relate to:
A.the calculation of marginal costs and marginal benefits of any economic activity.
B.the issue of determining causation.
C.the frequent inability of households and businesses to behave rationally.
D.the tradeoff problem associated with competing goals.
Answer:View Answer
2)Answer the question on the basis of the following list of assets:
Large-denominated ($100,000 and over) time deposits
Noncheckable savings deposits
Currency (coins and paper money) in circulation
Small-denominated (under $100,000) time deposits
Stock certificates
Checkable deposits
Money market deposit accounts
Money market mutual fund balances held by individuals
Money market mutual fund balances held by businesses
Currency held in bank vaults
Refer to the above list. Which of the following are considered to be “near-monies?”
A.items 2, 5, 8, and 9
B.all items except for 3
C.items 2, 4, 7, and 8
D.items 1, 5, and 10
Answer:View Answer
3)
Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, a rightward shift of the supply curve would:
A.appreciate the euro.
B.cause a surplus of euros.
C.decrease the equilibrium quantity of euros.
D.appreciate the dollar.
Answer:View Answer
4)At the output level defining allocative efficiency:
A.the areas of consumer and producer surplus necessarily are equal.
B.marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount.
C.consumer surplus exceeds producer surplus by the greatest amount.
D.the maximum willingness to pay for the last unit of output equals the minimum acceptable price of that unit of output.
Answer:View Answer
5)What are the two most important factors influencing investor preferences?
A.The desire for high rates of return and the thrill of uncertainty.
B.The desire for high rates of return and dislike of risk and uncertainty.
C.An equal balance between stocks and bonds, and high rates of return.
D.Stable rates of return and balance between private and public sector financial assets.
Answer:View Answer
6)What percentage of the U.S. adult population has at least a high school education (as of 2009)?
A.29 percent
B.41 percent
C.87 percent
D.95 percent
Answer:View Answer
7)In January 2010, the supply of money (M1) in the United States was about:
A.$847 billion.
B.$1,676 billion.
C.$1,365 billion.
D.$8,463 billion.
Answer:View Answer
8)Suppose a nation’s 2010 nominal GDP was $972 billion and the general price index was 90. To make the 2010 GDP comparable with the base year GDP, the 2010 GDP must be:
A.deflated to $678 billion.
B.deflated to $896 billion.
C.inflated to $1080 billion.
D.deflated to $1080 billion.
Answer:View Answer
9)
Refer to the above figures. Which figure(s) represent a situation where prices are sticky?
A.A only.
B.B only.
C.Both A and B.
D.Neither A nor B.
Answer:View Answer
10)Which one of the following would increase per unit production cost and therefore shift the aggregate supply curve to the left?
A.a reduction in business taxes
B.production bottlenecks occurring when producers near full plant capacity
C.an increase in the price of imported resources
D.deregulation of industry
Answer:View Answer
11)Consumption of fixed capital (depreciation) can be determined by:
A.adding taxes on production and imports to NDP.
B.subtracting NDP from GDP.
C.subtracting net investment from GDP.
D.adding net investment to gross investment.
Answer:View Answer
12)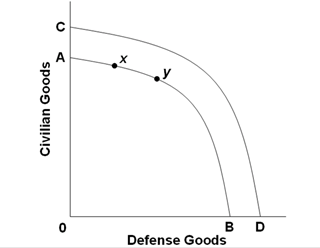
(Consider This) Refer to the above diagram. The U.S. response to the events of September 11, 2001, is illustrated by the:
A.shift of the production possibilities curve from CD to AB.
B.shift of the production possibilities curve from AB to CD
C.move from x to y on production possibilities curve AB.
D.move from y to x on production possibilities curve AB.
Answer:View Answer
13)
Refer to the above diagram in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. The equilibrium level of GDP in this economy:
A.is $400.
B.is greater than $400.
C.is less than $400.
D.cannot be determined from the information given.
Answer:View Answer
14)In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X, (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
Refer to the above. If X is an inferior good, a decrease in income will:
A.decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
B.decrease D, decrease P, and increase Q.
C.increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
D.increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
Answer:View Answer
15)Command systems are also known as:
A.market systems.
B.pure capitalism.
C.laissez-faire capitalism.
D.communism.
Answer:View Answer
16)The multiplier applies to:
A.investment but not to net exports or government spending.
B.investment, net exports, and government spending.
C.increases in spending but not to decreases in spending.
D.spending by the private sector but not by the public sector.
Answer:View Answer
17)The slope of a straight line can be determined by:
A.comparing the absolute horizontal change to the absolute vertical change between two points on the line.
B.comparing the absolute vertical change to the absolute horizontal change between two points on the line.
C.taking the reciprocal of the vertical intercept.
D.comparing the percentage vertical change to the percentage horizontal change between two points on the line.
Answer:View Answer
18)Economic growth rates in follower countries:
A.tend to be lower than in leader countries because labor forces in follower countries are too small.
B.tend to exceed those in leader countries because followers can cheaply adopt the new technologies that leaders developed at relatively high costs.
C.will never bring real GDP per capita up to the same levels as in leader countries, even if follower growth rates are greater than those in leader countries.
D.typically average about 2 percent per year.
Answer:View Answer
19)
Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. At the $200 level of GDP:
A.consumption is $200 and planned investment is $50 so that aggregate expenditures are $250.
B.consumption is $200 and planned investment is $100 so that aggregate expenditures are $300.
C.consumption is $250 and actual investment is $50 so that aggregate expenditures are $300.
D.aggregate expenditures fall short of GDP with the result that GDP will decline.
Answer:View Answer
20)Modern economic growth refers to countries that have experienced an increase in:
A.real GDP over time.
B.nominal GDP over time.
C.real output spread evenly across all sectors of the economy.
D.real output per person.
Answer:View Answer
21)If m equals the maximum number of new dollars that can be created for a single dollar of excess reserves and R equals the required reserve ratio, then for the banking system:
A.m = R – 1.
B.R = m/1.
C.R = m – 1.
D.m = 1/R.
Answer:View Answer
22)Free trade:
A.discourages growth by increasing competitive pressures on domestic firms.
B.encourages growth by effectively eliminating all patent and copyright barriers to growth.
C.discourages growth compared to situations where the government strongly controls foreign trade.
D.encourages growth by promoting the rapid spread of new inventions and innovations.
Answer:View Answer
23)The consumption and saving schedules reveal that the:
A.MPC is greater than zero, but less than one.
B.MPC and APC are equal at the point where the consumption schedule intersects the 45-degree line.
C.APS is positive at all income levels.
D.MPC is equal to or greater than one at all income levels.
Answer:View Answer
24)If the consumption schedule is linear, then the:
A.saving schedule will also be linear.
B.MPS will decline as income rises.
C.MPC will decline as income rises.
D.APC will be constant at all levels of income.
Answer:View Answer
25)Suppose government finds it can increase the equilibrium real GDP $45 billion by increasing government purchases by $18 billion. On the basis of this information we can say that the:
A.MPS in this economy is .4.
B.MPC in this economy is .4.
C.multiplier does not apply in this economy.
D.multiplier is 3.
Answer:View Answer
26)Evidence of a chronic balance of payments deficit is:
A.a decline in amount of the nation’s currency held by other nations.
B.an excess of exports over imports.
C.diminishing reserves of foreign currencies.
D.an increase in the international value of the nation’s currency.
Answer:View Answer
27)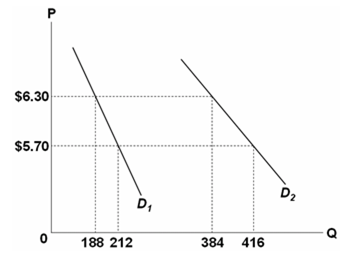
Refer to the above diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be:
A.0.8.
B.1.0.
C.1.2.
D.2.0.
Answer:View Answer
28)
Refer to the above data. In 2008 Transylvania realized a $1 billion surplus on goods and services.
Answer:View Answer
29)
Refer to the above table. The exchange rate in this market is:
A.8 luta for one dollar.
B.0.60 luta for one dollar.
C.6 luta for one dollar.
D.0.125 luta for one dollar.
Answer:View Answer
30)If the price of product L increases, the demand curve for close-substitute product J will:
A.shift downward toward the horizontal axis.
B.shift to the left.
C.shift to the right.
D.remain unchanged.
Answer:View Answer
31)
117.Refer to the above table. If this nation’s equilibrium price level is 125, its net exports will be:
A.minus $4 billion.
B.minus $2 billion.
C.zero.
D.$2 billion.
Answer:View Answer
32)Which of the following is a difference between stocks and bonds?
A.Bonds represent ownership; stocks represent debt.
B.Bonds make interest payments; stocks pay dividends.
C.Stock payouts are predictable; bond payouts are not.
D.All of these are differences between stocks and bonds.
Answer:View Answer
33)The above data show that:
A.Beta has a comparative advantage in producing chips.
B.Alpha has a comparative advantage in catching fish.
C.Alpha is subject to constant costs and Beta is subject to increasing costs.
D.Beta is more efficient than Alpha both in catching fish and in producing chips.
Answer:View Answer
34)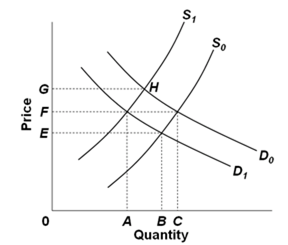
Refer to the above diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. A shift in the demand curve from D0 to D1 might be caused by a(n):
A.decrease in income if X is an inferior good.
B.increase in the price of complementary good Y.
C.increase in money incomes if X is a normal good.
D.increase in the price of substitute product Y.
Answer:View Answer
35)If the MPC in an economy is .9, a $1 billion increase in government spending will ultimately increase consumption by:
A.$1 billion.
B.$.9 billion.
C.$10 billion.
D.$9 billion.
Answer:View Answer
36)Increased present saving:
A.comes at the expense of reduced current investment.
B.comes at the expense of reduced current consumption.
C.can only occur if the government increases the amount of money in circulation.
D.is only possible if the economy is experiencing positive growth in real GDP.
Answer:View Answer
37)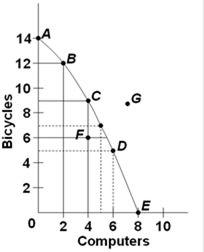
Refer to the above diagram. The combination of computers and bicycles shown by point G is:
A.attainable, but too costly.
B.unattainable, given currently available resources and technology.
C.attainable, but involves unemployment.
D.irrelevant because it is inconsistent with consumer preferences.
Answer:View Answer
38)The above data suggest that the amount of money demanded for transactions:
A.varies directly with the interest rate.
B.varies inversely with the interest rate.
C.varies inversely with nominal GDP.
D.is independent of the interest rate.
Answer:View Answer
39)Peter is saving money for a vacation he wants to take 5 years from now. If the trip will cost $1000 and he puts his money into a savings account paying 4 percent interest, compounded annually, how much would Peter need to deposit today to reach his goal without making further deposits?
A.$961.54
B.$923.75
C.$867.81
D.$821.93
Answer:View Answer
40)Bank panics:
A.occur frequently in fractional reserve banking systems.
B.are a risk of fractional reserve banking, but are unlikely when banks are highly regulated and lend prudently.
C.cannot occur in a fractional reserve banking system.
D.occur more frequently when the monetary system is backed by gold.
Answer:View Answer